Cambodia's health
○Overview
○Major diseases
○Medical situation in Cambodia (Nishino Tomoko doctor obstetrics and gynecology)
○State of health in Cambodia (AMDA doctor Cien security chapter representatives in Cambodia)
Overview
Cambodia's infrastructure has been delayed for about 30% of total population have access to safe drinking water, and about 17 percent use adequate sanitation facilities.
The inadequate garbage, cockroaches and mosquitoes, many mice, they are borne disease occurs. The hot and humid in this country is prone and bad food poisoning and gastrointestinal infections are diseases that require the most attention.
It is also now on the development of medical institutions. Questioning doctors and nurses to prescribe drugs due to auscultation, and blood tests are not many. Unable to investigate the cause of the disease, to prescribe multiple medications intended to cause some poor in Cambodia seems to put out a lot of patients receiving the drug.
Also, do not make so many more outpatient medical records for patients, and patients come to bring the results of ultrasound during practice and had previous prescriptions.
Medical examination that is limited to relief, the alien disease that requires hospitalization is equipped medical facilities in neighboring countries (Bangkok, Singapore, etc.) may also go.
Major diseases
Gastrointestinal infections and diarrhea are major symptoms, dysentery and typhoid are the most susceptible to illness and possibly hepatitis virus. As a mosquito-borne diseases malaria, dengue fever, Japanese encephalitis has.
Sexually transmitted disease (STD) are even more common. AIDS is spreading rapidly in Cambodia, and 4% to 5% of the population is said to be HIV positive, is a disease that most governments to focus on.
Of the 17,000 Cambodian people (about 2.7% of the total population) are HIV / AIDS are infected. Among them, the number of children aged 0 to 14 is estimated about 12,000 people. Estimated number of deaths in 2001, 12,000 people, orphans lost their parents due to this disease has been said about 55,000 people.
Medical situation in Cambodia
Nishino Tomoko doctor obstetrics and gynecology
AMDA Journal published from December 2004

A total of three months from October 2003 to participate in the project area Anroka Ken Yasushi Takeo Province, in July 2004 AMDA clinic in Phnom Penh, Cambodia (the ACC) held a three-month technical training in gynecological practice So I want to talk about the medical problems of Cambodia during this observation.
Low salaries in public health facilities
Which is causing a fundamental government policy that does not work, and its low salaries for civil servants in Cambodia. Low civil service salaries that are also due to rampant corruption, is also due to hold a public health care facilities, while there are many children attend the school, one of the reasons that there is no adequate education There. In other words, teachers who work in hospitals and school police, only to not get too fed Ino Yasushi life, or running on the side, or request the money is illegal. Underlying health center open year-round health care system, it is in principle open for 24 hours, many of the local health centers in the night or day, the gate has been closed. I dropped out and low salaries for staff, it has become impossible to open 24 hours.
Health workers, lack of specialist
In Cambodia have been killed intelligentsia in the civil war 20 years ago, doctors This midwife, and no most of the health professions such as nurses, doctors had survived at the end of civil war has been said about 20 people away. Also during the civil war in the absence of education, health system also collapsed. Compensate the lack of an absolute number, with most of the work as a general practitioner medical doctor educated after the Civil War.
Fewer specialists in hospital departments and even Phnom Penh is inadequate for the specialized area of training medical students. You noticed I was talking with health professionals in Cambodia, the less overall knowledge of the disease life-threatening disease or a small number of patients and diseases of clinical psychiatric practice, in particular nurses have been educated almost seemed not.
The absence of testing
Japanese doctors do not feel sorry for the inspection, a hard time in Cambodia. Interview a doctor or nurse, and basic medical care that is to prescribe drugs such as stethoscope, blood tests can be done and there are not many. For imaging, the facility has been increasing X-ray examination and ultrasound can be, to laboratory level testing does not seem to have made much progress. As a gynecologist, in spite of the large proportion of the total patients with gynecological inflammatory diseases, venereal disease testing has hardly suffered from the status quo.
No medical records
In Cambodia, the idea is probably not make a lot of facilities for patients with outpatient medical records. ACC is away at medical records. Patient care and bring it to the ultrasonography results and previous medical prescription when asked. This is the place of the chart. There is also described that does not require medical records, patient enough not to interview. I myself have Mamanarazu speak Khmer to gather information, which has continued to suffer.
Problems with the patent medicine
ACC can now examine in more patients with infertility. Because, in Cambodia that lady doctor to treat infertility is the special few. In Cambodia the fertility is kind of what has been done, Clomid is a drug popular as available over the counter most of what you are taking the liberty of individuals, or that prescribed by a doctor in general This still remains a mystery.
To get anything over the counter drugs, pills or Depo-Provera has been bought from a pharmacy (for the injectable contraceptive), I met a lot of patients with bleeding and amenorrhea cause after using. They did not seem to explain most of the time of purchase by the drug. In Cambodia, it seems that many problems due to medication by people with no knowledge of a patent medicine.
Many current drugs out of Cambodia
The Ministry of Health recommends that the proper use of antibiotics in a medical facility. In this context, there are currently many antibiotics prescribed many facilities. For example, it has been common antibiotic that is prescribed to patients with 4-3 kinds of inflammatory diseases. That can not be examined to find the cause, even going on inflammation, there is also reason to prescribe multiple medications intended to cause some in Cambodia under the patient's put out a lot of drugs Another reason seems to be that poor.
This lack of
Noteworthy that after the civil war in Cambodia is that many of the lost books of this burn up the policy of Pol Pot. Finally just recently started publishing activities, this book was written in Khmer medicine so there is little relationship. Medical education in Cambodia has been made in French, the French medical books are difficult to get enough, there are not many medical books. Training of physicians in the urgent, anxious where medical education is what's going on.
How to Support People
As well as aid from abroad, many of the policies of the Ministry of Health in Cambodia, is a way of sending only the medical institution. For those medical equipment, we can not send only the soft hard, if not use it actually becomes a waste of money. The medical device may be a major force in the region to raise the level of medical care is required in terms of soft cover always enough. You can not use the equipment as they are I hope that Japan can not fully considered. A very good example of the medical device has been working since aid will introduce you to the ACC. The ultrasound equipment donated by Japan in obstetrics and gynecology hospital has been active in the 1997 ACC. Doctor's security director who studied in France, ultrasound, diagnostic technology is acknowledged. Thus, another NGO that is often a request from the public and ultrasound. Also, this machine is also used for training other physicians. In Japan, this model is old and I can see almost disappeared, while receiving little in Cambodia repairs are still doing great.
This creates a health
We write the story of one self-praise. ACC ACC during his stay with the help of a full, finished version of the Khmer maternal and child health education booklet. Future, I think I want to use in various situations, and published in Cambodia and wants to read the general and women. If you are interested 存Jimasu Itadaketara and let me know.
I wrote discursively. Since I first visited Cambodia five years ago, initially involved in school construction aid, this year we have worked AMDA medical assistance. Aid to Cambodia where you lose more you know. I really do what you are going out now but I want trouble. AMDA Headquarters everyone, AMDA to everyone in Cambodia, I accept that Itadakimashita support, we are grateful.
State of health in Cambodia
AMDA doctor Cien security chapter representatives in Cambodia
(Huzii Shizuko translation)
AMDA Journal published from August 2003

▲The author (Dr. Shienriti)
I. Introduction

▲Clinic Tour
Kingdom of Cambodia (the "countries") is an agricultural country located in Southeast Asia. Western Thailand, Laos and Thailand to the north and the Gulf of Thailand to the south, east and borders the Vietnam border. The total land area of 181,035 square kilometers, from east to west across the widest place about 580km, 450km in the North and South. The climate is tropical countries, the underlying rhythm of rural life, is divided by two very different winds. 11 February, the cold, dry winds blowing from the northeast, the rain hardly rains. However, the summer monsoon winds that blow from the southeast, high humidity, causing heavy rains. The average annual temperature of 27 degrees in the capital Phnom Penh, April is the hottest, daily maximum temperature of 40 degrees or so.

▲Sightseeing in Angkor
The population of countries is about 13.4 million people (according to 2002), of which 84% are in rural areas, the remaining 16 percent live in urban areas. This country's population density is 64 people per square kilometer. Recent social development, the result of industrial development in particular, the huge influx of migrants from rural areas to cities seeking work or business opportunities, resulting in a decrease in the number of rural areas and workers productivity that.
II. Current health
Description:
Social production base countries, human resources, social services and the years of civil war and 20 were destroyed by political instability and economic depletion, is being slowly rebuilt. However, most residents living in poor rural areas is now not blessed with access to even the most basic health services. In more than half the population under the age of 18, have been very concerned about issues of their economic and social welfare. The challenge to improve the position of children and women are still a lot. HIV / AIDS epidemic may have started relatively late, and then rapidly progress countries have now become one of the countries in Southeast Asia are most affected. HIV / AIDS and economic damage to each home and give individuals the problem is very large. UN Children's Fund (UNICEF) assistance with the skills to get a better life for young people to express themselves, safer, more meaningful learning how to live, to help school-age children stabilize their lives, noting in particular the children go to school, creating an environment that promotes child-friendly learning environment.
1.Maternal and Child Health:
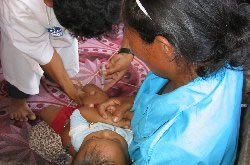
▲Maternal and Child Health
About one in ten babies born in the country, has met not die for a birthday. The infant mortality rate is 95 per 1,000 people, higher as well for children under five mortality, 124 per 1,000 males. This is the highest number among the ASEAN countries. In addition, 40% did not receive basic vaccinations Satoru Shika children, immunization rates of children under 12 to 23 months is currently still low. And children under 5 years old to about 45%, and growth retardation are seen as underweight. In children 6 to 59 months, only 57% of vitamin A has been paid to nutrition reinforcing agent. Rate of low birth weight newborns at birth was 11 percent. Households using only 14% of iodine salt. Maternal mortality is 437 per 100,000 people, access to professional medical organization for maternal relatively low. During pregnancy, women who received screening by trained health workers is only 38% of the total. In addition, women who had childbirth care by medical personnel is only 32 percent. The remaining 68% are women, laboring under the assistance of traditional midwives in the home. In addition, postpartum women who receive care, especially in rural areas, is very rare. Dangerous abortion rate in the past five years, very high.
2.Public health facilities:
Only 30% of total population have access to safe drinking water, 17 percent use adequate sanitation only.
3.HIV/AIDS:

▲Health Education
During the first quarter of 2002 from 2001, UNAIDS (UNAIDS) World Health Organization (WHO), in cooperation with institutions and governments, HIV / AIDS reviewed the estimates of people living together. Review This estimate was published in 1997 and 1999, and many recent HIV / AIDS is based on research trends. The method has been developed with the cooperation of the international expert group, HIV infection rates, AIDS incidence, mortality due to HIV infected mothers were used to determine the number of infected children. In addition, countries with low infection rates, infections are concentrated in the country regions and layers, the country has spread throughout the country infected, HIV different methods were used to estimate the infection rate. The current estimation, and accurately reflect the number of infected persons can not say that to improve research methods, in accordance with as much information can be collected, these estimates are constantly being modified. In these reports, which are subject to men and women aged 15 to 49 years. This age group are considered the most sexually active age. Risk of HIV infection but does not continue after the age of 50 apparently, most people tend to take action risks essentially an exaggeration to think of being infected before the age of 50 are not. When calculating adult HIV infection rates, population aged 15 to 49 years this has been used as the denominator.
In fact, out of 17,000 people in Cambodia (2.7 percent of the total population) have HIV / AIDS are living with. Among them, the number of children aged 0 to 14 is estimated about 12,000 people. Estimated number of deaths in 2001, 12,000 people, orphans lost their parents due to this disease has been said about 55,000 people.
4.Tuberculosis and Malaria:
Countries is one of the countries most TB patients in the world. Incidence of tuberculosis symptoms, including 540 males per every 100,000 people. Mortality from tuberculosis is 90 per 100,000 people, out of 203 TB patients, HIV prevalence is 11.8%. The incidence of malaria is 8 per 1,000 people. The two diseases have lost their lives and many people say thousands of people every year.
5.Socio-economic, education, and poverty:
The per capita GDP is estimated to be about US $ 297, the annual growth rate of about 5 percent. Approximately 36 percent of the population is estimated to live below the poverty line (income of less than $ 1 per day), poverty gap is very large. Adult male literacy rate is 80% and 57% in women, the rate of women attending university or higher education institutions is very low compared with men.
6.Mine:
The protracted civil war, creating a large number of people with disabilities, the number is still increasing continuously. Socio-economic survey of 1997, 25,805 people with disabilities has become a conflict for the Cambodian people. In addition, it was another 16,290 people disabled by landmines. This is proof that the injured were directly related to the history of the war in this country of one out of every 250 Cambodians. Disease (polio, congenital malformations) and accidents (traffic accidents, accidents at work and home), to append a lot of people with disabilities also amount to thousands of other causes.
Only 10 percent of landmine victims only, and is said to have received adequate health services. Yet countries are estimated to have been sleeping underground mines and millions of thousands of unexploded bombs. The lives of people with disabilities due to accident thousands.
Educational opportunity for them, it is very difficult to find a job, has become a major obstacle to health problems in human resource development. Moreover, the important issue is the placement of human resources and medical facilities. If decentralization is proceeding, although human resources professionals are especially concentrated in the capital cities, remote areas in the public / health care facilities lack both health workers and private facilities.
7.Efforts AMDA:
▲AMDA Clinic Cambodia
Decentralization of health services, improvements in organizational management financial system to promote health through improved human resource development, the government over the country trying to dig up the past years. And bilateral aid, international organizations, NGOs, has also received support from other agencies and health conditions have not been much improvement yet. Especially for maternal and child health situation, changes are hardly seen the last five years.
According to a survey by Oxfam, the cost of family health services spent $ 29 a year, which Niatari GDP 11 percent of that country is said to be one of the greatest health burden in the world. Medical expenses, in many homes, the largest spending hits. 46% of people who recently lost their land, the debt is due to medical expenses related to (hence the vicious cycle of poverty.)
To assist countries in rebuilding health care systems that were destroyed by years of civil war and conflict 20, AMDA in 1992 (after the national settlement with the Paris Peace Agreements, and all the opposition), the first project started was. Human resource development, construction of medical facilities repair, provision of medicines and medical supplies, management and primary / other related activities through the secondary health care, and community health system reconstruction assistance. Rebuilding health systems in the process of the AMDA countries, particularly maternal and child health, with an emphasis on prevention and spread of infectious diseases and drug administration, as well as training community health workers, a new technical support and advice to role.
Recently AMDA is a new framework type "contract" in the pilot project health services, providing health services OD (Operational District: District Government, Primary / classification of health administration is responsible for secondary medical care) and management skills of Through improving the quality of aid has played an important role. In particular, the human resources / capacity building responsibilities to local staff, procurement of medical drugs and medical supplies, building and health facilities, construction of health care systems, health systems as a model for future countries We have developed a. 12 years and started the project in the country soon. AMDA will help the government rebuild the country for health care systems, spared the hard work. The many successful projects in the area, to prove it.
I fear that we are international organizations, NGOs, the problem imposed on cooperation from all donors and international agencies, "the sustainability of the project" is. And all the people of this country, in order to provide better health services for future'd think everyone in government partnership with private donors.
III.Conclusion:
Finally, the matters summarized in four points we should consider countries want to conclude.
1) rebuild the health care system. (Past 10 years, has been carried out to rebuild health systems in more efficient, public acceptance, to a system and a persistent need for further efforts to find new ways and mechanisms a).
2) a group of people known as the poor and socially disadvantaged, access to health service activation.
3) HIV / AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria, nutrition, maternal and child health, gender equality, improving educational opportunities offered to the problems of women and girls.
4) Improving the social and economic conditions. (This is of paramount importance not to think seriously we do. If If you can earn a little people are poor, can send someone to school kids, when you are sick to the hospital take it, it will be able to eat enough and eat.

▲To help children

▲Children Playing




